1. 应用LGR二氧化碳同位素分析仪,通过测定肠易激综合症患者的呼出气体中的13CO2和12CO2的同位素分子比率,可以对患者体内小肠细菌过度生长情况做出正确诊断 Diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome patients using high-precision stable 13CO2/12CO2 isotope ratios in exhaled breath Show Affiliations J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2014,29, 1918-1924 Hydrogen breath tests (HBT) are widely used for the diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). However, the conclusions drawn from these studies are highly controversial, and several discrepancies exist in the results. The aim of our study is to develop an alternative 13C-glucose breath test (13C-GBT) methodology by measuring high-precision 13CO2/12CO2 isotope ratios in exhaled breath to accurately diagnose SIBO using an optical cavity-enhanced CO2 isotope analyzer. In all, 118 diarrhea-predominant (IBS-D) patients diagnosed according to ROME III criteria underwent 13C-GBT and HBT following the ingestion of a test meal containing 50 mg 13C-enriched glucose with 50 g glucose. The excretion of 13CO2 enrichments and a cumulative percentage dose of 13C-recovered (c-PDR) significantly depleted (p < 0.001) for the positive SIBO patients (n = 25) compared to the patients with negative SIBO (n = 53) as diagnosed by HBT. A cut-off value of 5.47‰ at 45 min was indicative of a positive SIBO syndrome. Subsequently, a portion of IBS-D individuals (n = 20) whose HBTs were negative but 13C-GBTs were positive, suggesting HBT often fails to diagnose SIBO when the patients may have “non-hydrogen-producing” bacteria. 13C-GBT also correctly diagnosed SIBO in patients (n = 20) within the “grey-zone” and during the preclinical phase of SIBO as opposed to HBT. The prevalence of SIBO with IBS-D in Indian population was estimated to be 45.7%. Our study demonstrates 13C-GBT, for the first time, as a clinically valid and sufficiently robust alternative diagnostic methodology for an accurate evaluation of SIBO in IBS-D patients and superior to HBT. 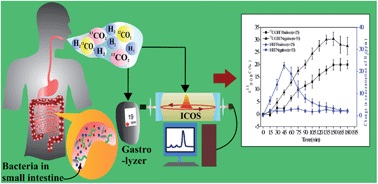 2. 13C尿素呼气试验排泄动力学:内部产生和药物恢复的CO2对幽门螺杆菌感染的诊断准确性的影响 Excretion kinetics of 13C-urea breath test: influences of endogenous CO2 production and dose recovery on the diagnostic accuracy of Helicobacter pylori infection Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, September 2014, Volume 406, Issue 22, pp 5405-5412 Suman SomAffiliated withDepartment of Chemical, Biological and Macromolecular Sciences, S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences Abhijit MaityAffiliated withDepartment of Chemical, Biological and Macromolecular Sciences, S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences Gourab Dutta BanikAffiliated withDepartment of Chemical, Biological and Macromolecular Sciences, S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences Chiranjit GhoshAffiliated withDepartment of Chemical, Biological and Macromolecular Sciences, S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences Sujit ChaudhuriAffiliated withDepartment of Gastroenterology, AMRI Hospital Sunil Baran DaschakrabortyAffiliated withDepartment of Gastroenterology, AMRI Hospital Shibendu GhoshAffiliated withDepartment of Medicine, Vivekananda Institute of Medical Sciences Manik PradhanAffiliated withDepartment of Chemical, Biological and Macromolecular Sciences, S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic SciencesThematic Unit of Excellence on Nanodevice Technology, S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences Email author
Abstract We report for the first time the excretion kinetics of the percentage dose of 13C recovered/h (13C-PDR %/h) and cumulative PDR, i.e. c-PDR (%) to accomplish the highest diagnostic accuracy of the 13C-urea breath test (13C-UBT) for the detection of Helicobacter pylori infection without any risk of diagnostic errors using an optical cavity-enhanced integrated cavity output spectroscopy (ICOS) method. An optimal diagnostic cut-off point for the presence of H. pylori infection was determined to be c-PDR (%) = 1.47 % at 60 min, using the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis to overcome the “grey zone” containing false-positive and false-negative results of the 13C-UBT. The present 13C-UBT exhibited 100 % diagnostic sensitivity (true-positive rate) and 100 % specificity (true-negative rate) with an accuracy of 100 % compared with invasive endoscopy and biopsy tests. Our c-PDR (%) methodology also manifested both diagnostic positive and negative predictive values of 100 %, demonstrating excellent diagnostic accuracy. We also observed that the effect of endogenous CO2 production related to basal metabolic rates in individuals was statistically insignificant (p = 0.78) on the diagnostic accuracy. However, the presence of H. pylori infection was indicated by the profound effect of urea hydrolysis rate (UHR). Our findings suggest that the current c-PDR (%) is a valid and sufficiently robust novel approach for an accurate, specific, fast and noninvasive diagnosis of H. pylori infection, which could routinely be used for large-scale screening purposes and diagnostic assessment, i.e. for early detection and follow-up of patients. 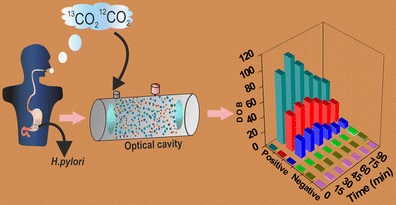 Figure The excretion kinetics of the 13C-urea breath test with an ICOS system is demonstrated for accurate, specific, fast and noninvasive diagnosis of H. pylori infection in the human stomach |